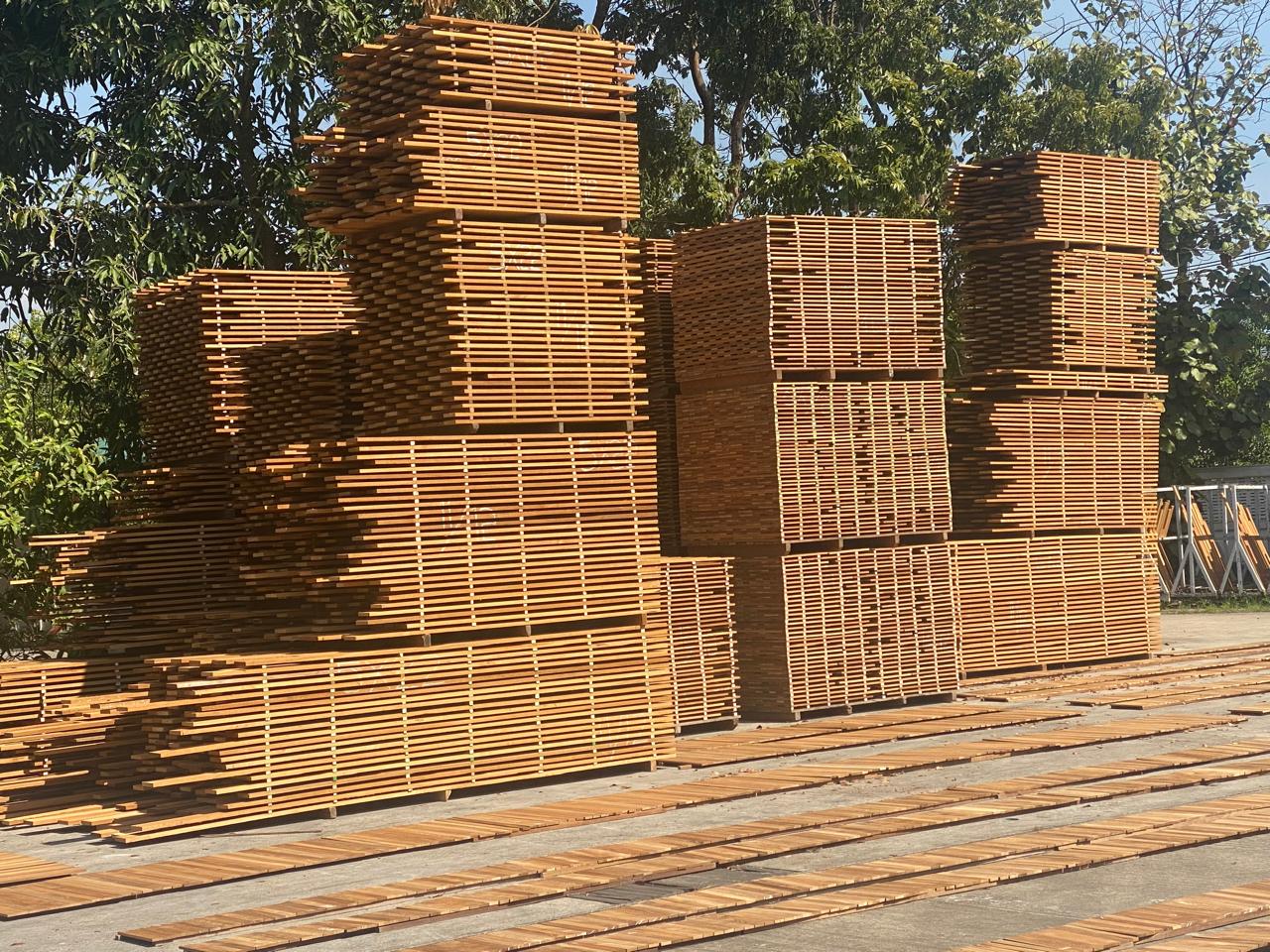
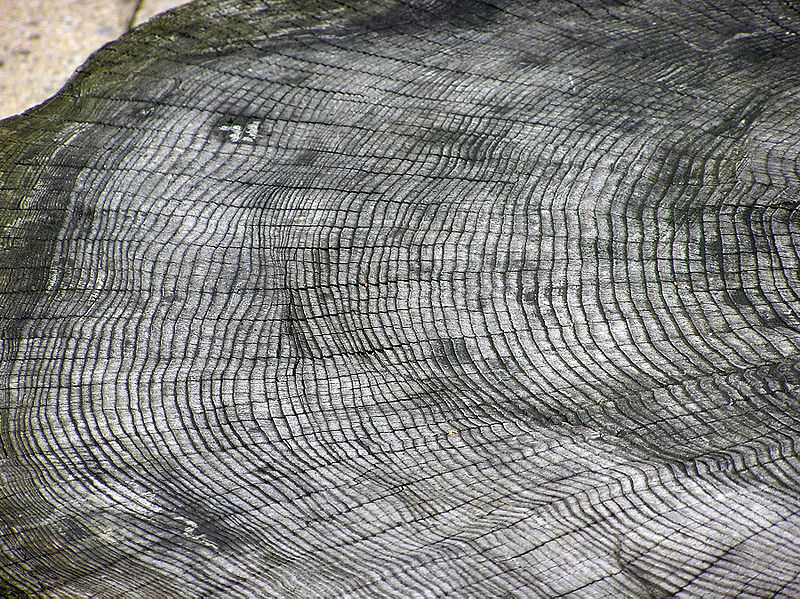
Air drying is one of the most traditional and cost-effective methods used to reduce the moisture content in timber. It involves exposing freshly cut wood to natural air circulation, allowing the moisture to evaporate over time. This process is crucial in preparing timber for various uses, ensuring that the wood becomes stable and durable for construction, furniture making, or other applications.

How Air Drying Works
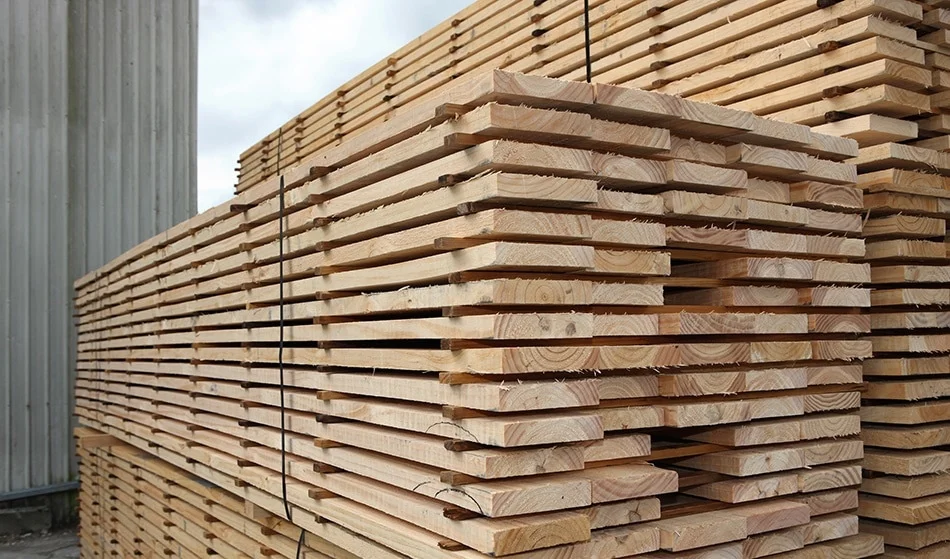
The air-drying process begins after timber is harvested and sawn into manageable sizes. The wood is then stacked in a specific arrangement to promote efficient air circulation. Key elements of this arrangement include:
Proper Stacking: Timber pieces are stacked with spaces (known as stickers) between them. This ensures that air flows freely around each piece.
Location: The drying area must be well-ventilated, protected from direct sunlight, rain, and excessive humidity to prevent rapid drying or cracking.
Orientation: Timber stacks are often oriented in a way that takes advantage of prevailing winds to enhance airflow.
Proper Stacking: Timber pieces are stacked with spaces (known as stickers) between them. This ensures that air flows freely around each piece.
Location: The drying area must be well-ventilated, protected from direct sunlight, rain, and excessive humidity to prevent rapid drying or cracking.
Orientation: Timber stacks are often oriented in a way that takes advantage of prevailing winds to enhance airflow.
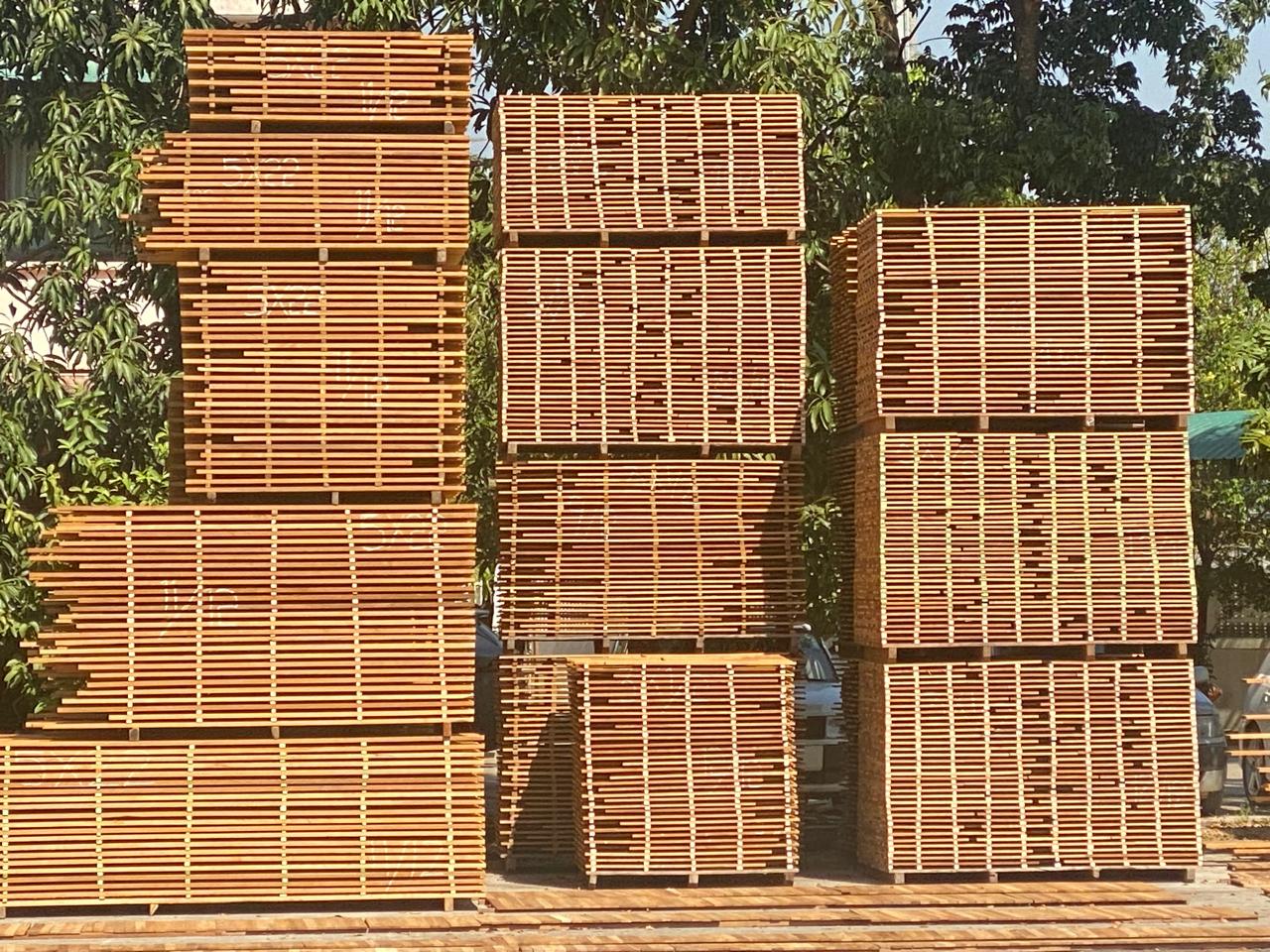
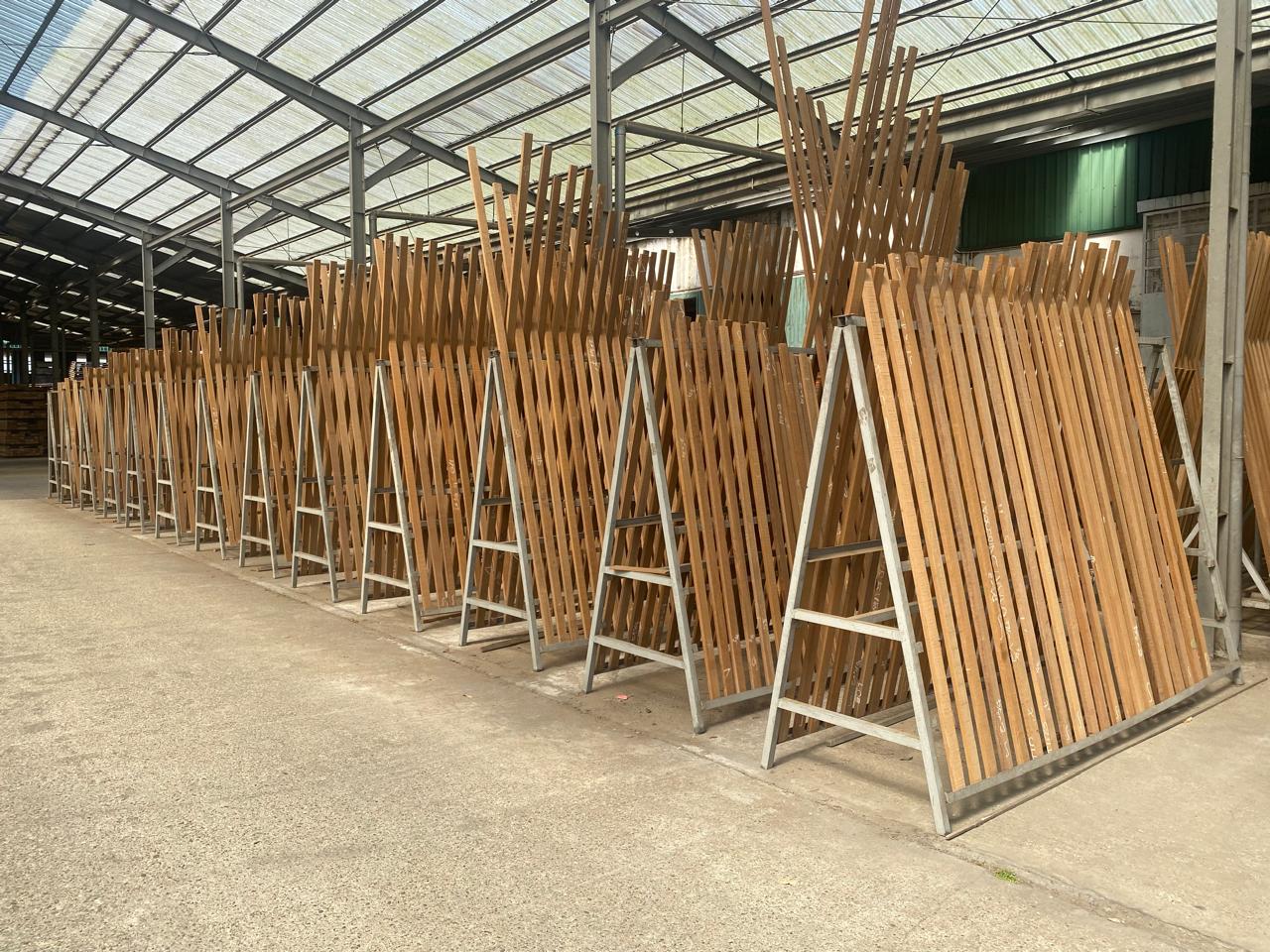
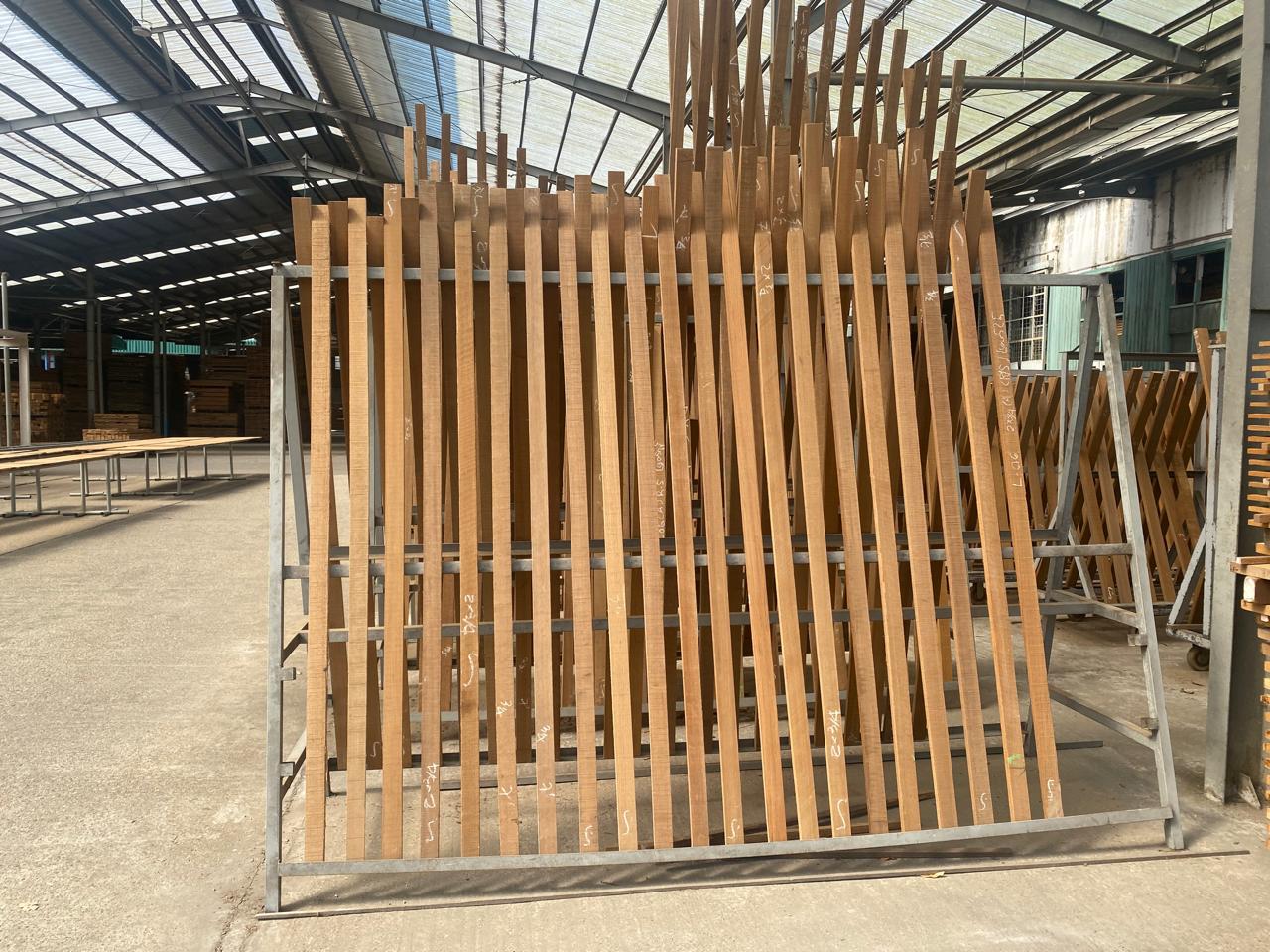



Benefits of Air Drying
Air drying offers several advantages for the timber industry:
Cost-Effective: It requires minimal equipment, making it an economical choice for smaller-scale operations or traditional timber yards.
Eco-Friendly: Since it relies on natural air circulation, it does not require electricity or fuel consumption, making it environmentally sustainable.
Improved Quality: Gradual moisture removal minimizes the risk of warping, splitting, or other defects that can occur with faster drying methods.
Cost-Effective: It requires minimal equipment, making it an economical choice for smaller-scale operations or traditional timber yards.
Eco-Friendly: Since it relies on natural air circulation, it does not require electricity or fuel consumption, making it environmentally sustainable.
Improved Quality: Gradual moisture removal minimizes the risk of warping, splitting, or other defects that can occur with faster drying methods.
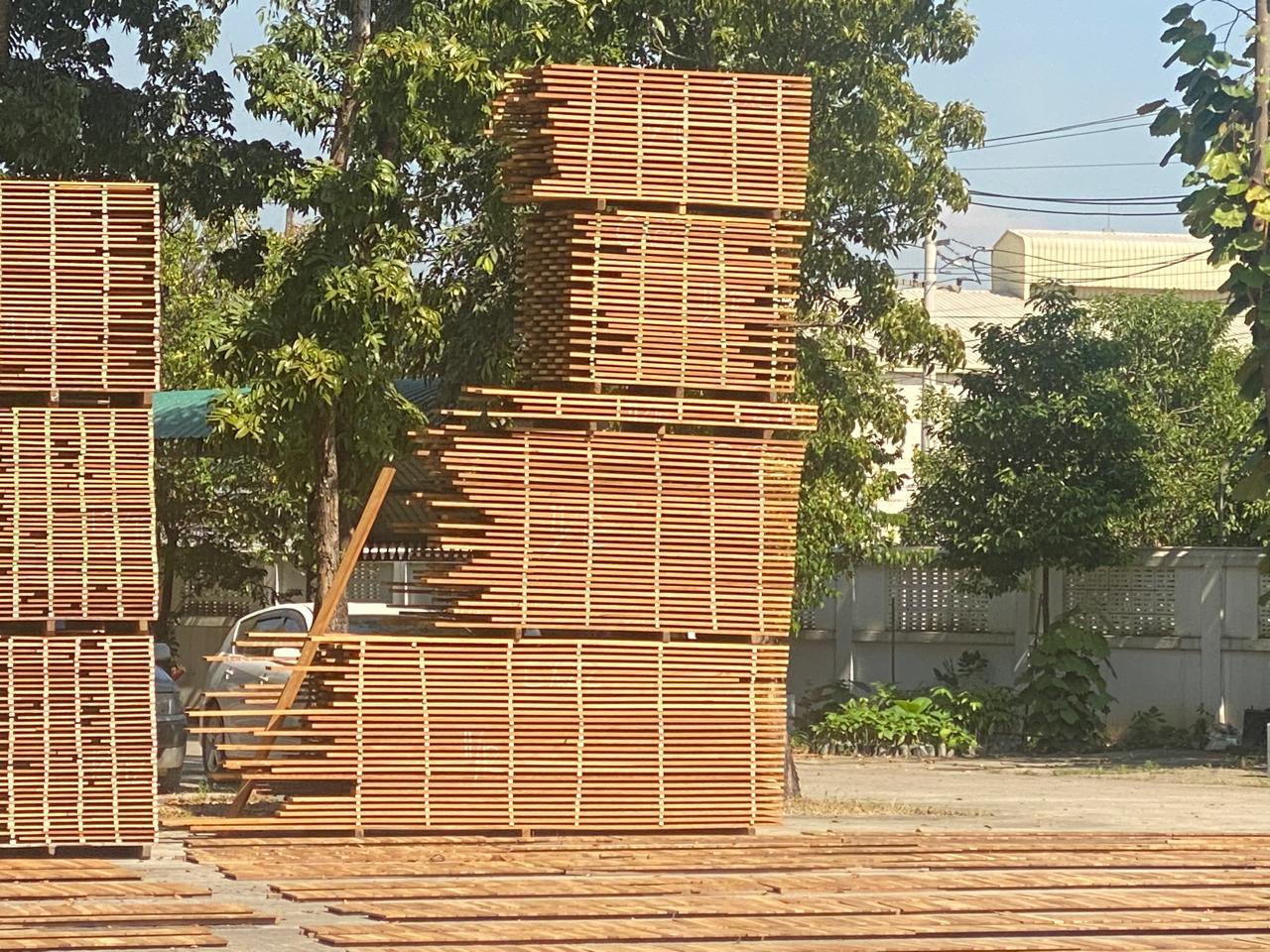

Challenges of Air Drying
Despite its advantages, air drying comes with certain limitations:
Time-Intensive: The process can take several months to years, depending on the type of wood and environmental conditions.
Weather Dependence: Unpredictable weather, such as excessive rain or humidity, can delay the drying process or lead to uneven drying.
Limited Control: Unlike kiln drying, air drying does not allow precise control over moisture content, making it less suitable for applications requiring extremely dry wood.
Time-Intensive: The process can take several months to years, depending on the type of wood and environmental conditions.
Weather Dependence: Unpredictable weather, such as excessive rain or humidity, can delay the drying process or lead to uneven drying.
Limited Control: Unlike kiln drying, air drying does not allow precise control over moisture content, making it less suitable for applications requiring extremely dry wood.
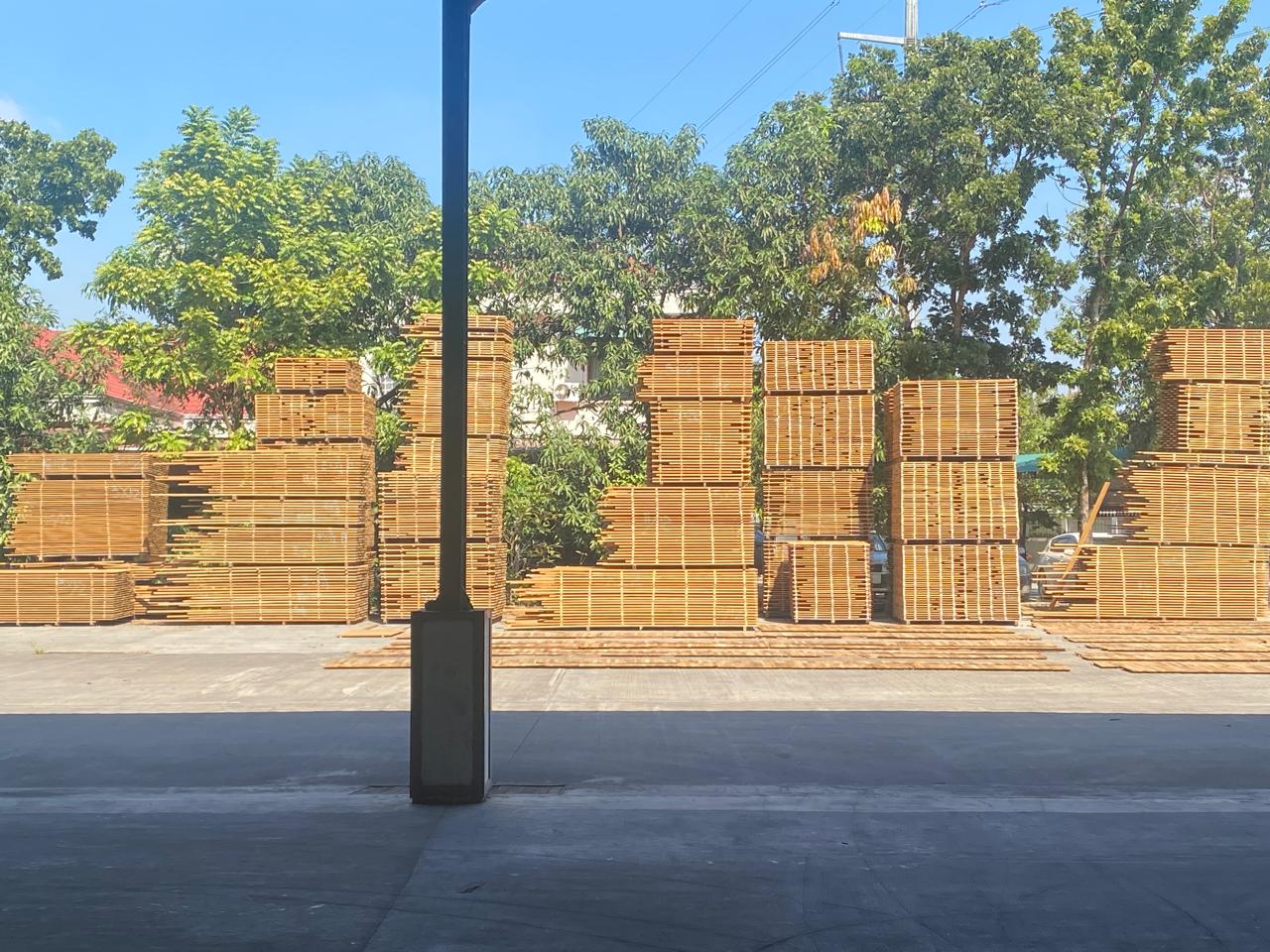

Conclusion
Air drying remains an essential method in the timber industry, especially for those who value cost-efficiency and eco-friendliness. While it may require patience and careful management, the quality and sustainability of air-dried timber make it a preferred choice for many craftsmen and builders. For industries that aim to balance tradition and functionality, air drying is a timeless and reliable technique.