Wood is one of the most versatile and widely used natural resources on the planet. Its renewability is one of its defining characteristics, but it also plays a significant role in shaping its environmental impact. When managed properly, wood’s renewability makes it a key ally in the fight against climate change and environmental degradation. However, its sustainability depends on how responsibly it is sourced and used. In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the environmental impact of wood’s renewability and what it means for a sustainable future.

What Does Wood’s Renewability Mean?
Wood is considered renewable because it comes from trees, which can regrow naturally. Unlike non-renewable materials such as metals or fossil fuels, which take millions of years to form, trees can regenerate within decades through natural growth cycles or reforestation efforts. This makes wood a renewable resource, provided forests are managed responsibly to allow continuous replenishment.
Environmental Benefits of Wood’s Renewability
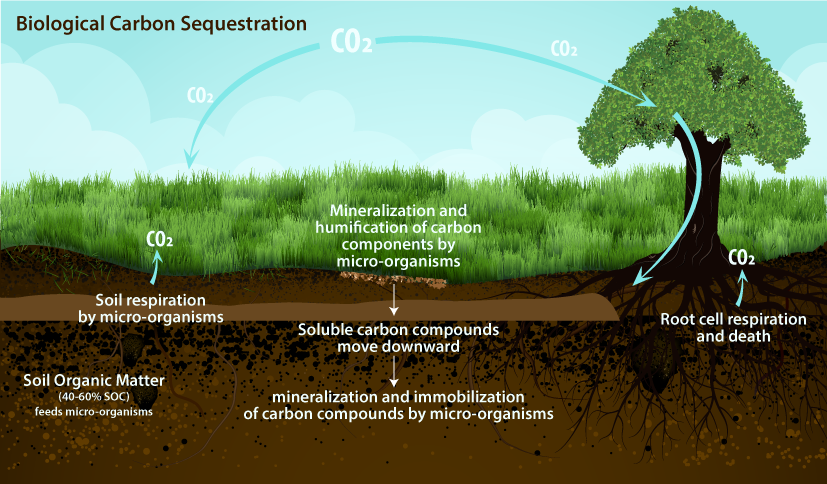
✅Carbon Sequestration : Trees act as natural carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and storing it in their biomass. When harvested sustainably, wood products like furniture or building materials continue to store this carbon for decades, helping to offset greenhouse gas emissions.
✅Reduced Dependency on Non-Renewable Materials : By replacing energy-intensive materials like steel, concrete, or plastic with wood, industries can reduce their environmental impact. The renewable nature of wood ensures a steady supply, unlike finite materials that deplete over time.
✅Low Energy Footprint : Processing wood requires less energy compared to materials like concrete and steel. This means less fossil fuel use and fewer emissions, aligning with global efforts to reduce energy consumption and fight climate change.
✅Forest Conservation Incentives : Sustainable harvesting of renewable wood encourages landowners to maintain forests rather than clearing them for agriculture or development. Healthy forests provide habitats for wildlife, regulate water cycles, and prevent soil erosion, benefiting ecosystems as a whole.
✅Reduced Dependency on Non-Renewable Materials : By replacing energy-intensive materials like steel, concrete, or plastic with wood, industries can reduce their environmental impact. The renewable nature of wood ensures a steady supply, unlike finite materials that deplete over time.
✅Low Energy Footprint : Processing wood requires less energy compared to materials like concrete and steel. This means less fossil fuel use and fewer emissions, aligning with global efforts to reduce energy consumption and fight climate change.
✅Forest Conservation Incentives : Sustainable harvesting of renewable wood encourages landowners to maintain forests rather than clearing them for agriculture or development. Healthy forests provide habitats for wildlife, regulate water cycles, and prevent soil erosion, benefiting ecosystems as a whole.

The Role of Sustainable Forestry in Wood’s Renewability
While wood is inherently renewable, its renewability depends on how forests are managed. Unsustainable logging, illegal harvesting, and overexploitation can turn wood from a renewable resource into an environmental threat. Therefore corrective measures like replanting and regeneration, selective logging, promoting biodiversity and forest certification programs help in this.
Challenges to Wood’s Renewability
Despite its potential, wood’s renewability faces challenges:
✅Deforestation : Unsustainable practices, such as illegal logging and clear-cutting, lead to deforestation, resulting in habitat loss, soil degradation, and increased carbon emissions.
✅Illegal Logging : Unregulated harvesting undermines efforts to manage forests sustainably, threatening wood’s status as a renewable resource.
✅Overharvesting : Harvesting wood faster than forests can regenerate depletes resources and causes long-term ecological harm.
✅Climate Change : Climate change affects forests’ ability to regenerate by altering rainfall patterns, increasing the frequency of wildfires, and spreading diseases that harm trees.
✅Deforestation : Unsustainable practices, such as illegal logging and clear-cutting, lead to deforestation, resulting in habitat loss, soil degradation, and increased carbon emissions.
✅Illegal Logging : Unregulated harvesting undermines efforts to manage forests sustainably, threatening wood’s status as a renewable resource.
✅Overharvesting : Harvesting wood faster than forests can regenerate depletes resources and causes long-term ecological harm.
✅Climate Change : Climate change affects forests’ ability to regenerate by altering rainfall patterns, increasing the frequency of wildfires, and spreading diseases that harm trees.
The Future of Wood’s Renewability
The future of wood as a renewable resource is promising, but it requires a collective effort from governments, industries, and consumers. Innovations in forestry management, increased adoption of sustainable practices, and stronger regulations against illegal logging can ensure that wood continues to be a renewable and eco-friendly resource.
As we look toward a more sustainable future, wood’s renewability highlights the importance of balancing human needs with environmental stewardship. By supporting responsible forestry and making mindful choices, we can harness the benefits of wood without compromising the planet’s health.
As we look toward a more sustainable future, wood’s renewability highlights the importance of balancing human needs with environmental stewardship. By supporting responsible forestry and making mindful choices, we can harness the benefits of wood without compromising the planet’s health.
Conclusion
Wood’s renewability is a powerful advantage in the global effort to reduce environmental impact and build a sustainable future. By prioritizing sustainable forestry, protecting biodiversity, and supporting ethical sourcing practices, we can ensure that wood remains a renewable and responsible choice for generations to come.
Are you ready to make sustainable choices in your wood usage? Let’s work together to preserve this invaluable resource!
Are you ready to make sustainable choices in your wood usage? Let’s work together to preserve this invaluable resource!